Brain Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): Understanding the Cause, Symptoms & Treatment Options
As an Interventional Neuroradiologist, I frequently encounter patients with concerns regarding brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs).
In this blog, we will address few common questions relating to brain arterio-venous malformations (BAVMs).
What is Brain Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
Brain Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins in the brain.
Unlike normal blood vessels, AVMs lack the capillary network, causing abnormal shunting of blood from arteries to veins. This disrupts the delicate blood flow balance in the brain, potentially leading to serious complications.
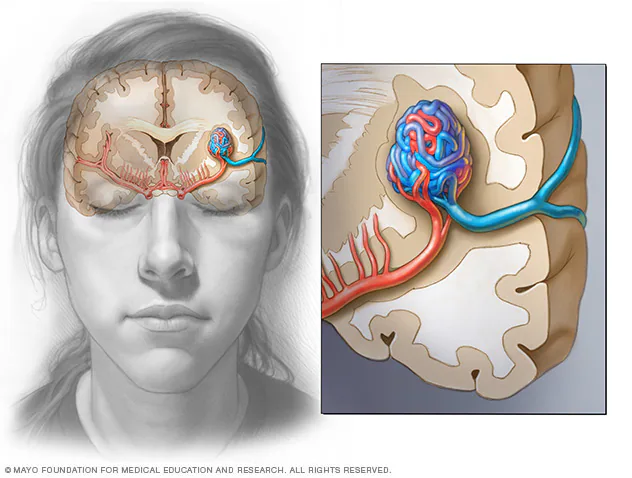
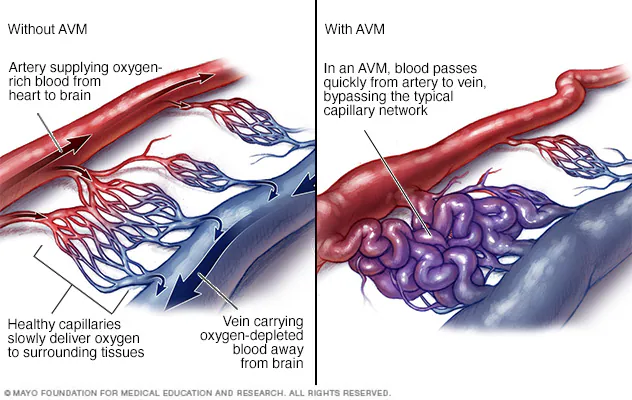
Can AVM happen outside the brain?
Yes, AVM can be present anywhere in the body. Being trained in Vascular & Interventional Radiology (VIR) and Interventional NeuroRadiology (INR), I have treated AVMs in different parts of the body like brain, spine, lungs, intestines, uterus, hands and legs.
What are Causes of AVM?
The precise cause of AVM is unknown. Following causes are involved:
- Genetic factors: Some individuals may inherit a predisposition to AVM.
- Developmental abnormalities: AVMs may develop during fetal development or infancy.
- Trauma: Head injury or trauma to the brain can trigger the formation of AVM.
- Risk factors: Factors such as high blood pressure and smoking may increase the risk of bleeding from an AVM.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformations
Symptoms of AVM vary depending on its size, location, and whether it has ruptured (bled). A lot of times AVM may go undetected as they cause no symptoms.
Common symptoms, if they occur, may include:
- Headaches: Often severe and persistent
- Seizures
- Neurological deficits: Weakness, numbness, or vision problems
- Intracranial haemorrhage (bleeding inside brain): Sudden, severe headache, vomiting, loss of consciousness
- Other symptoms: Memory problems, difficulty speaking, and cognitive impairment.
It is important to get an early assessment done if you experience these symptoms.
How to diagnose Brain AVM?
Diagnosis of AVM typically involves:
- Clinical evaluation: Neurological examination to assess symptoms and deficits, that may guide further tests to confirm underlying cause like AVM.
- Imaging tests: MRI, CT scan to confirm presence, location, bleeding from AVM.
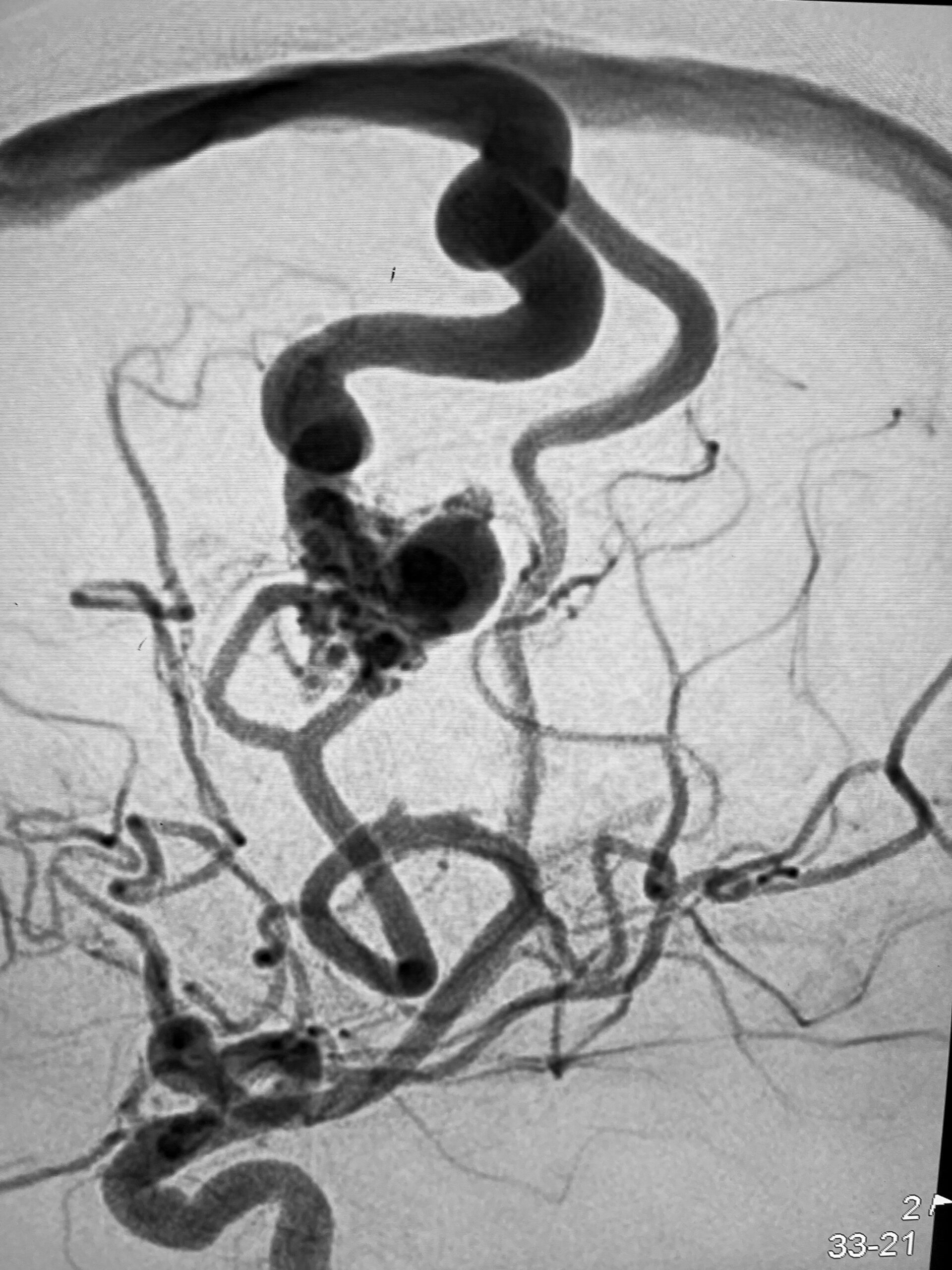
- Cerebral Angiography (DSA): To study the AVM architecture in detail & guide treatment decision. Very small AVM that may be not seen on CT, MRI can be detected with DSA. This is performed by an Interventional Radiologist / Interventional NeuroRadiologist.
Early diagnosis & detailed assessment is very important to understand AVM in detail, its risk factors and formulate treatment strategy accordingly.
What are Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformation?
Decision-making: Treatment choice depends on the AVM’s size, location, patient’s overall health & any complications that AVM may have caused.
- Conservative management: Monitoring and medication to control symptoms.
- Interventional procedure Embolization: Blocking the abnormal blood vessels with angiography techniques. Small tubes or catheters are used to go deep into the AVM. Once inside the AVM, glue like liquid embolic agents (Onyx, Squid, NBCA, etc.) are injected which causes closure of these abnormal blood vessels. It is a minimally invasive procedure done through a small injection from wrist or groin artery by an Interventional NeuroRadiologist / Interventional Radiologist.
- Radiosurgery: Targeted radiation from outside to shrink the AVM over time.
- Surgical resection: Open brain surgery to remove the AVM.
- Combined: Many times, a combination of interventional embolization, open surgery & radiation are used to achieve cure. A detailed discussion between your Interventional NeuroRadiologist, Neurosurgeon, Radiation expert will help tailor the treatment strategy best suited for you.
Brain AVM Treatment in Mumbai
Dr Amit Sahu is an Interventional NeuroRadiologist / Interventional Radiologist practising across various hospitals in Mumbai.
He possesses extensive experience in treating AVMs using advanced techniques like endovascular embolization.
He offers comprehensive care for brain AVM treatment working with a team involving neurologist, neurosurgeons, radiation experts, intensivist offering all aspects of AVM treatment. Mumbai offers access to one of the most advanced medical facilities equipped to provide comprehensive care for AVM patients.
Arteriovenous Malformations Doctors in Mumbai
If you have concerns about a brain AVM, seeking a consultation with a qualified specialist is crucial. You may schedule an appointment to discuss your individual situation & what is the treatment option most suitable for you.
Conclusion
Brain AVMs are abnormal tangles of blood vessels that can disrupt blood flow in the brain. While the cause remains unknown, early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
If you have been diagnosed with an AVM, do consult an interventional neuroradiologist / interventional radiologist to understand the role of minimally invasive embolization procedure for AVM.